CNC Milling and Turning: Knowing the Key Differences for Better Manufacturing
Did you know manufacturers can reduce up to 30% of their manufacturing time once they have chosen the right CNC process? They can also eliminate a significant amount of their operational costs. Today, the decision between CNC milling and turning is not merely technical; it is strategically important because it affects the efficiency, quality, and price of the entire manufacturing operation.
This article outlines the differences between CNC milling and turning, describing their specific characteristics, advantages, and ideal conditions for application. It is indispensable for both newcomers to CNC machining and industry experts searching for ways to improve productivity.
What is CNC Milling?
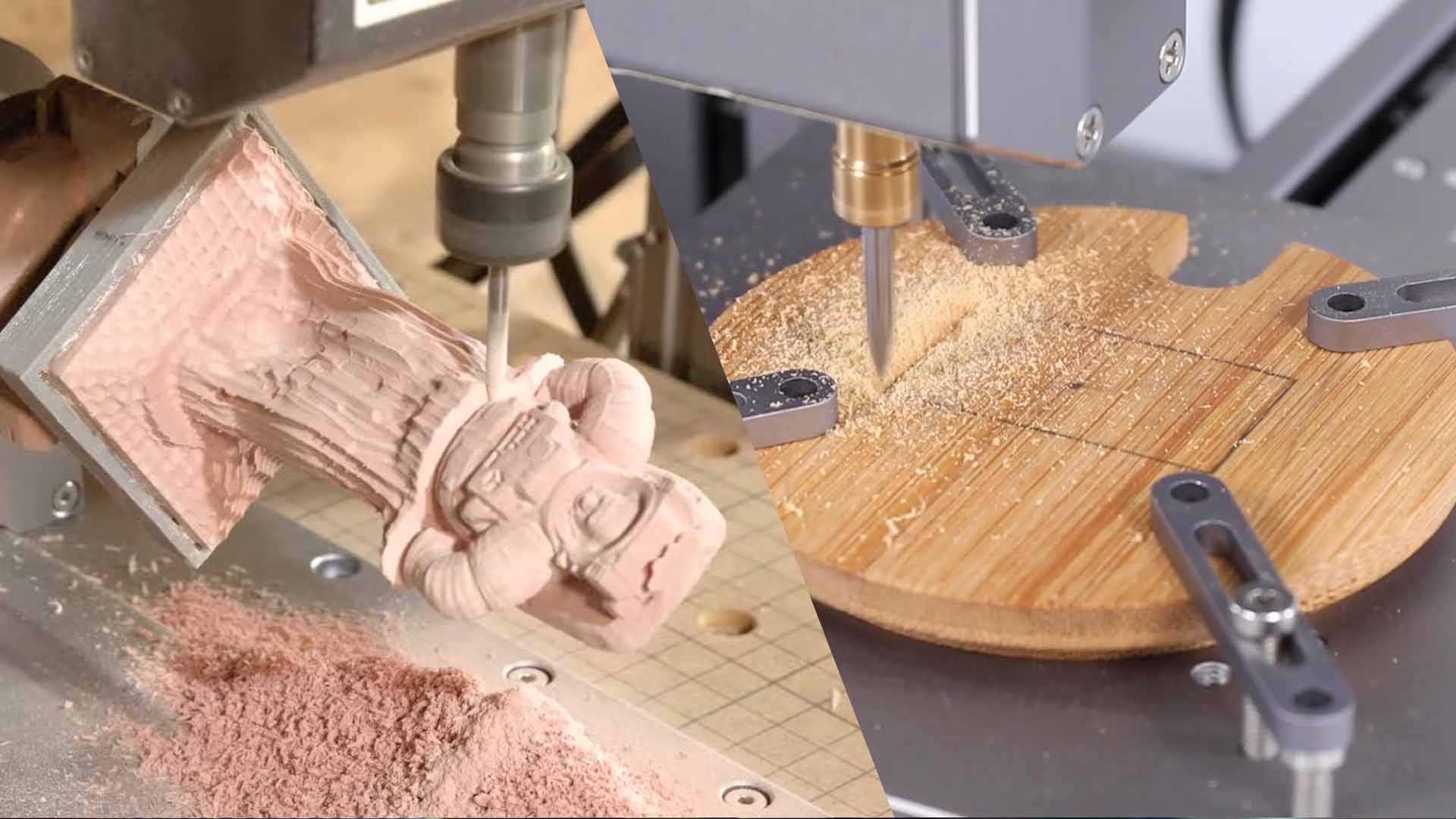
CNC milling is a subtractive processing method in which rotating cutting tools are moved in or along multiple axes while the workpiece remains fixed. A CNC machine is best used for parts with very complex geometries, intricate contours, and detailed surfaces.
CNC milling machines can perform all the cutting movements on the workpiece, usually having 3-4-5 axes. They are highly capable of producing very accurate cuts onto any material with a tremendous volumetric removal rate. They’re great for tough metals, plastics, composites, etc.
CNC milling is handy across various industries, from aerospace and automotive to medical and electronics, since it can produce complex and detailed components. Additionally, it involves higher tooling and setup costs, making it less cost-effective for straightforward, high-volume production.
What is CNC Turning?
CNC turning machine is a method where the workpiece rotates while a cutting tool moves along its surface. It is most helpful in manufacturing cylindrical and symmetrical components, such as shafts, bolts, or nozzles, because all lathes perform operations mainly in 2 axes (X and Z), albeit superior machines can possess more capabilities.
CNC turning machining is highly efficient for producing round parts like shafts, bushings, and tubes. The main advantages of CNC turning are speed, improved economics over purely manual processes for long runs, and much better surface quality on all cylindrical parts.
CNC turning does not cater to anything but round or symmetrical parts, so it is not particularly well suited for very complex or even non-cylindrical designs. It is also specifically best at producing smooth, accurate surfaces; complex shapes that require multi-direction cutting are more difficult for this machine.
Detailed Comparison: CNC Milling and Turning
Here’s a detailed comparison of CNC milling and turning.
1. Fundamental Difference: The primary difference lies in the movement. CNC milling is the process of cutting a workpiece utilizing rotating tools revolving around a fixed framework from which intricate shapes can be machined. In contrast to this, while CNC turning allows the workpiece to be rotated, the tool travels along its surface, which is most applicable for cylindrical parts.
2. Machine Design & Setup: Generally, milling machines possess a multi-axis system (3-, 4-, or 5-axis) for cut intricacies. However, the turning machine was designed to spin the workpiece on X and Z axes.
3. Tooling & Cutting Strategies: Milling uses rotating cutters to shape the workpiece from various angles. Turning uses a stationary cutting tool to cut material from the rotating workpiece.
4. Geometric Capability: Multidimensional CNC milling is perfect for complicated shapes that have holes and contours within the piece. CNC turning would most likely be used to manufacture cylindrical and symmetrical parts such as shafts or rods.
5. Surface Finish & Tolerance: Because it cuts continuously, turning produces smoother finished surfaces. Milling may require additional finishing to match the turning’s smoothness. Both processes achieve high precision but turning excels in tight tolerances for round parts.
6. Production Efficiency: CNC milling with intricate designs is best for low-to-medium volume production. CNC turning is more efficient for high-volume production of round parts.
Now, here’s something cool: with the rise of desktop manufacturing, CNC milling is becoming more accessible than ever. Take Snapmaker, for example—a multi-function device that combines CNC carving (kind of like mini-milling) with 3D printing and laser engraving. It’s an affordable option for hobbyists and small workshops. Snapmaker’s modular design lets you easily swap out function modules, like switching from 3D printing to CNC carving, so you can tackle complex shapes without breaking the bank. Plus, it comes with user-friendly software (like Snapmaker Luban) and a supportive community, making it super easy to get started.

On the flip side, CNC turning is more efficient for making cylindrical parts, but it’s not as flexible as milling. If your project involves a variety of shapes and sizes, CNC milling (or something like Snapmaker’s CNC carving feature) might be the better way to go.
Applicable Scope and Decision-Making Tips
The main question is when to choose CNC milling vs turning. Here’s how you can choose the ideal option.
Decision-Making Factors:
Part Geometry: Choose CNC milling for complex designs; use CNC turning for cylindrical parts.
Production Volume: CNC turning is ideal for high-volume production, while CNC milling suits custom or low-volume parts.
Material Considerations: Milling works well with diverse materials, whereas turning is often preferred for metals.
Tolerance & Surface Finish: CNC turning achieves better finishes on round parts; milling is better for intricate details.
CNC milling example: An aerospace company needing intricate turbine blade designs will opt for milling.
CNC turning example: A manufacturer producing thousands of precision shafts will use turning for efficiency.
Pros & Cons Summary Table:
| Terms | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| CNC Milling | -Creates precise parts.-Fast and efficient.-Compatibility with various materials.-Highly affordable | -High material wastage.-Not enough qualified technicians. |
| CNC Turning | -Produces accurate parts.-Safe process.-Compatible with various materials.-Fast and efficient.-Ensures consistency in batches. | -High setup costs.-Size restrictions.-High material wastage. |
Conclusion
The key difference between CNC milling and turning lies in how the material is processed: milling moves the cutting tool while turning rotates the workpiece. Each method has distinct advantages depending on part complexity, volume, and material needs.
Choosing the right CNC process can boost efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality. Evaluate your project requirements carefully and strategically decide to optimize manufacturing performance.
What are your experiences with CNC milling and turning? Let us know in the comments!