How to Store and Dry 3D Printer Filaments
3D printing is really exciting, but proper 3D printer filament storage is responsible for the quality of your prints. Keeping the filament free from moisture, especially for moist-sensitive materials such as nylon, PVA, and TPU ensures the print consistency is maintained. Getting it exposed to moist air, dust, or dirt will alter your prints and produce suboptimal quality. Moisture causes the filaments to swell and weaken, resulting in stringy, brittle prints and poor adhesion.
Therefore, if you are wondering how to dry filament and store it well, the guide is for you.
In this article:
- Best Methods for Storing 3D Printer Filament
- How to Dry Filament: Nylon, PVA, TPU
- All in One: Filament Dryer Dock and Storage Box
- Identifying Wet Filament
Best Methods for Storing 3D Printer Filament
Filament storage requires a proper approach so that filaments will be good in quality and durable. The two prime factors that influence filament storage are temperature and humidity. You need to prevent your filaments from moisture as moisture in the air weakens filaments.
Storage conditions vary by filament so, first of all, check the manufacturer’s instructions in the packaging and follow them for optimal storage. Here are some universal storage ways.
Airtight Containers
You may choose airtight containers such as kitchen zip bags, or plastic storage bins – they prevent moisture from entering into the container and affecting filament quality.
Original Package
If your filament is in a resealable bag, check for a zip lock before you open it. After you’re done, pack the spool back in its original bag with a new silica pack to keep it dry.
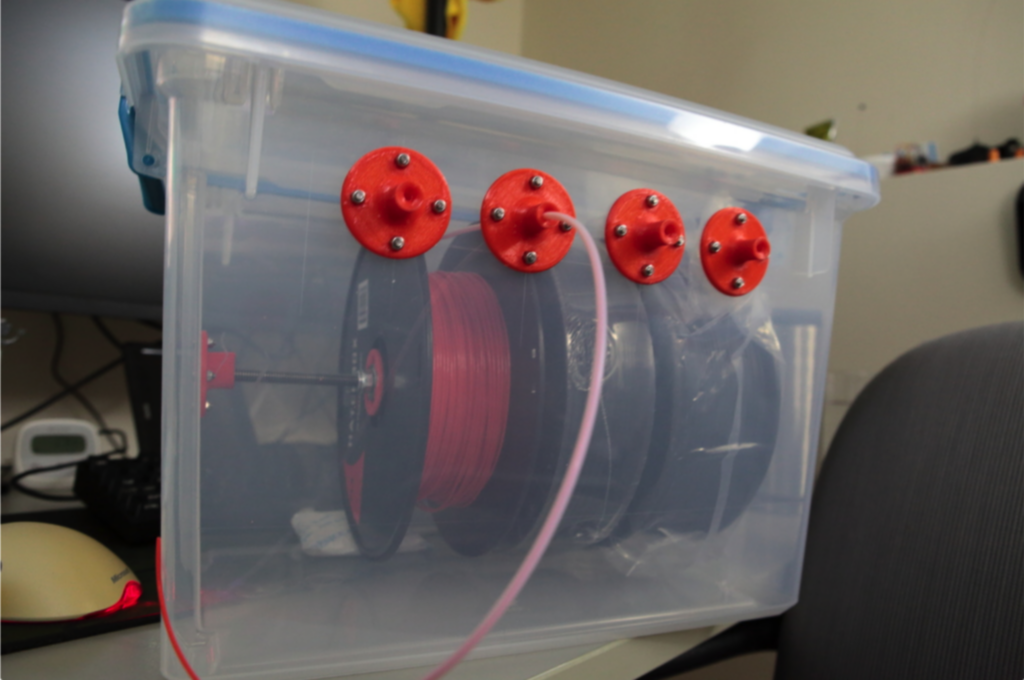
DIY Solutions for Filament Storage
The following are some DIY solutions for 3D printer filament storage boxes.
Materials
For this, you need the following materials.
- Airtight plastic containers or vacuum-sealable bags with zippers
- Silica gel packets or rechargeable desiccants
- Hygrometer (optional, to measure humidity)
Instructions
- Choose a Container: Use moisture-proof containers, such as airtight bins or vacuum-sealed bags, for the spools of filament.
- Include Desiccant: Silica gel or another type of desiccant can be placed in the container or bag, but it is best to frequently update or recharge your desiccant for best results.
- Sealing and Storing: Wind the filament neatly and seal the box or the bag tightly enough to prevent air from going inside. Store in an environment with humidity less than 40% using a hygrometer, if possible.
How to Dry Filament: Nylon, PVA, TPU
In case you are wondering how to dry filament safely, you can consider these subsequent options.
DIY Filament Drying Methods
Ovens are commonly found in any home. However, there are some things to note while drying filaments in a conventional oven.
Home ovens are usually poor at maintaining a specific temperature, especially a low temperature. It may overheat and melt your filament, especially for PLA and other temperature-sensitive filaments. Therefore, you may consider using a blast (forced air) for better constant temperature.
Another method of drying is to adapt a food dehydrator to run an internal filament spool. Most of these conversions are done by removing the trays between the layers and placing the filaments in. These only appear to provide relatively low temperatures, so do consider the temperature at which you will need to dry your filament before you commit to buying one.
Dedicated Filament Dryers
You can have a dedicated filament dryer that not only ensures dry filaments but also extracts the moisture from the filaments.
Heated spool containers do great jobs as well by preserving the temperature and ensuring that humidity and moisture do not cause effects on the filaments.
Drying Techniques: Temperature and Time
If you dry your filaments beyond these temperatures, they will become soft and melt into one another. The recommended drying temperatures for common 3D printing filaments are as follows; note: only for reference.
| PLA | 40 °C–48 °C (104 ℉–118.4 ℉) |
| TPU | 45 °C–55 °C (113 ℉–131 ℉) |
| ABS, Nylon | 60 °C–80 ℃ (140 ℉–176 ℉) |
| PETG | 60 °C–70 °C (140 ℉–158 ℉) |
| PC | 120 °C–130 °C (248 ℉–266 ℉) |
The actual drying times of filaments will depend on the additives added to the filaments, as well as the initial water content levels in the filaments and the ambient temperature and humidity.
You must note that these temperatures are general guidelines, and you should consult the manufacturer’s instructions for more precise recommendations specific to the particular filament.
Identifying Wet Filament
If your filament is wet or contains moisture inside, then you may experience the following symptoms.
- You tend to hear popping or cracking sounds when extruding
- The strength of the part as well as how one layer adheres to another are greatly minimized
- Lines of extrusion irregular
- Stringing, blobbing, or oozing very evident
- Print surfaces are untypically textured, “fuzzy”
All in One: Filament Dryer Dock and Storage Box
Properly storing and drying 3D printer filaments is crucial for maintaining print quality. The SnapDryer offers a practical solution: filament drying and storage. Designed by Snapmaker in collaboration with Polymaker, it features a Dryer Dock and a Storage Box that work together to ensure filaments stay dry and ready for use. The Dryer Dock is equipped with precise temperature and humidity control, removing moisture from filaments to prevent printing issues like poor adhesion or warping. The Storage Box is designed to store filaments in a controlled environment, maintaining consistent dryness and protecting them from exposure to air and humidity. This combined solution makes it easier to keep filaments in optimal condition, ensuring more reliable and successful 3D prints. Learn more on Snapmaker x Polymaker Present: The SnapDryer.
Final Thought
For you to get the best prints from your 3D printer, you need to maintain your 3D printer filaments and ensure they are not moist. Best maintenance practices help you to print premium quality objects while also extending the lifespan of your 3D printer.